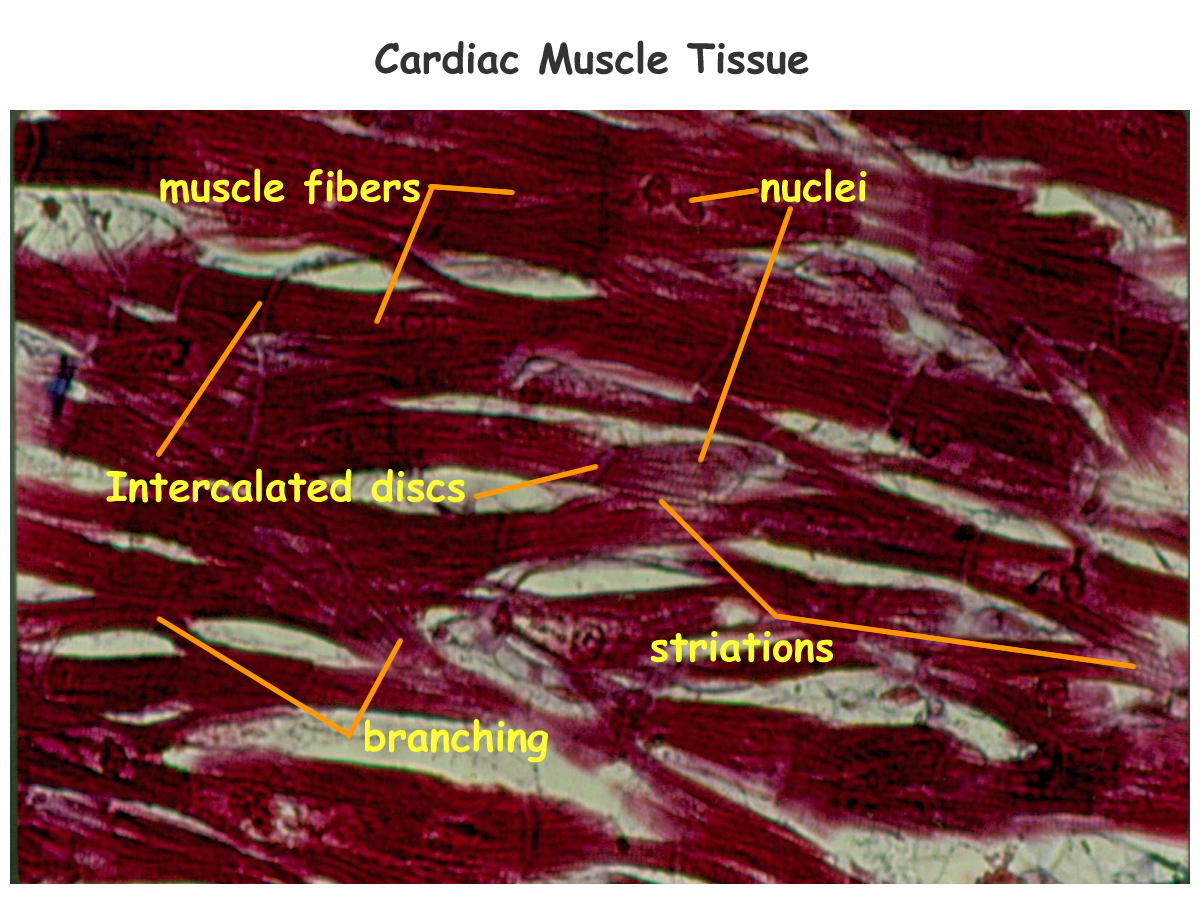
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Slide Labeled
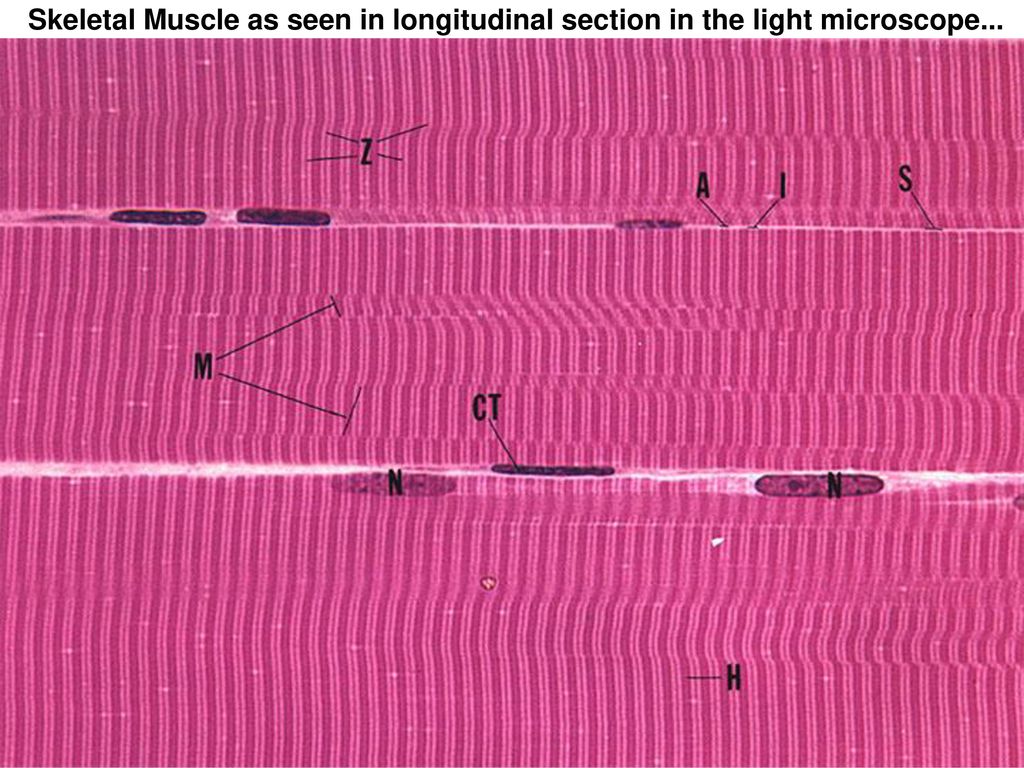
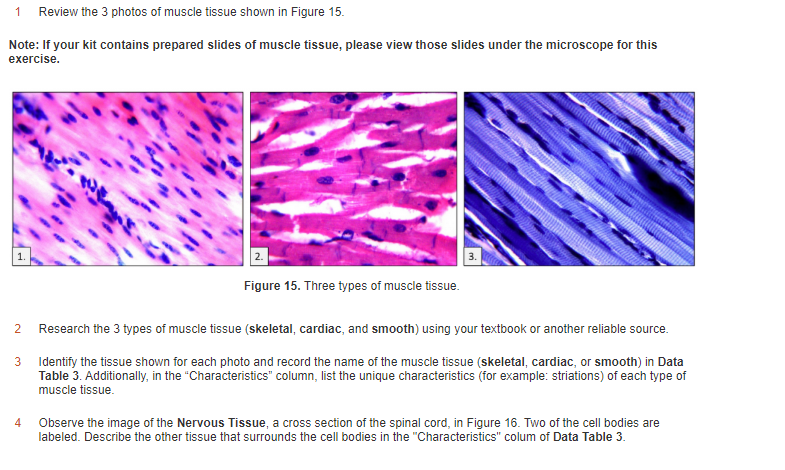
The interior of a skeletal muscle cell is filled with the structures involved in contraction myofibrils sarcoplasmic reticulum t tubules mitochondria etc.
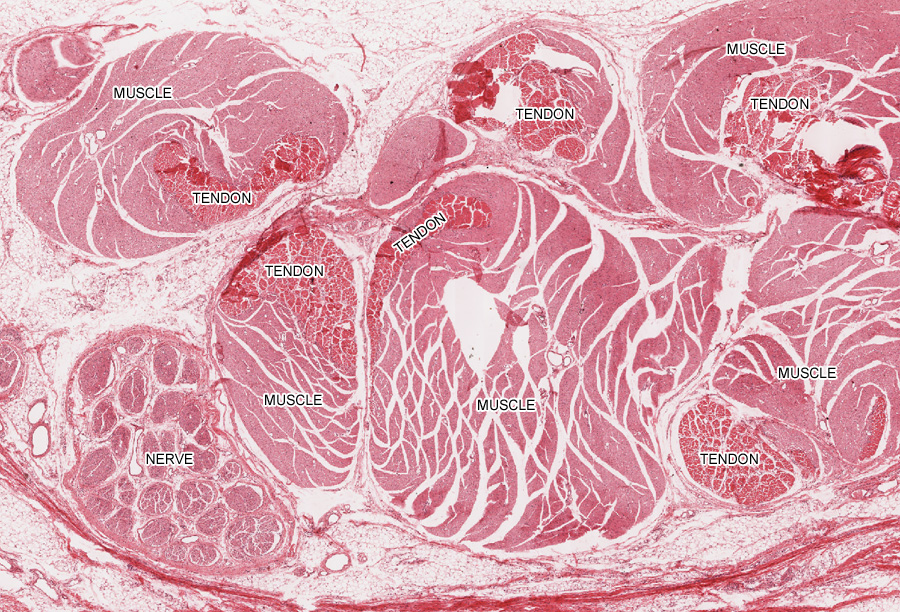
Skeletal muscle tissue slide labeled. In skeletal and cardiac muscle these thick and thin filaments are organised in series into sarcomeres along the length of the muscle cell. Epimysium outer tissue. Skeletal cardiac and smooth muscle all contract using the same mechanism. Skeletal muscle is an excitable contractile tissue responsible for maintaining posture and moving the orbits together with the appendicular and axial skeletonsit attaches to bones and the orbits through tendons.
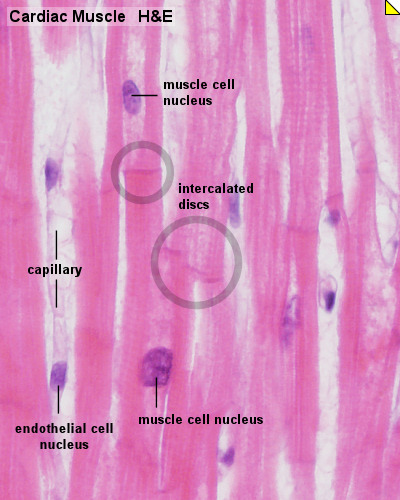
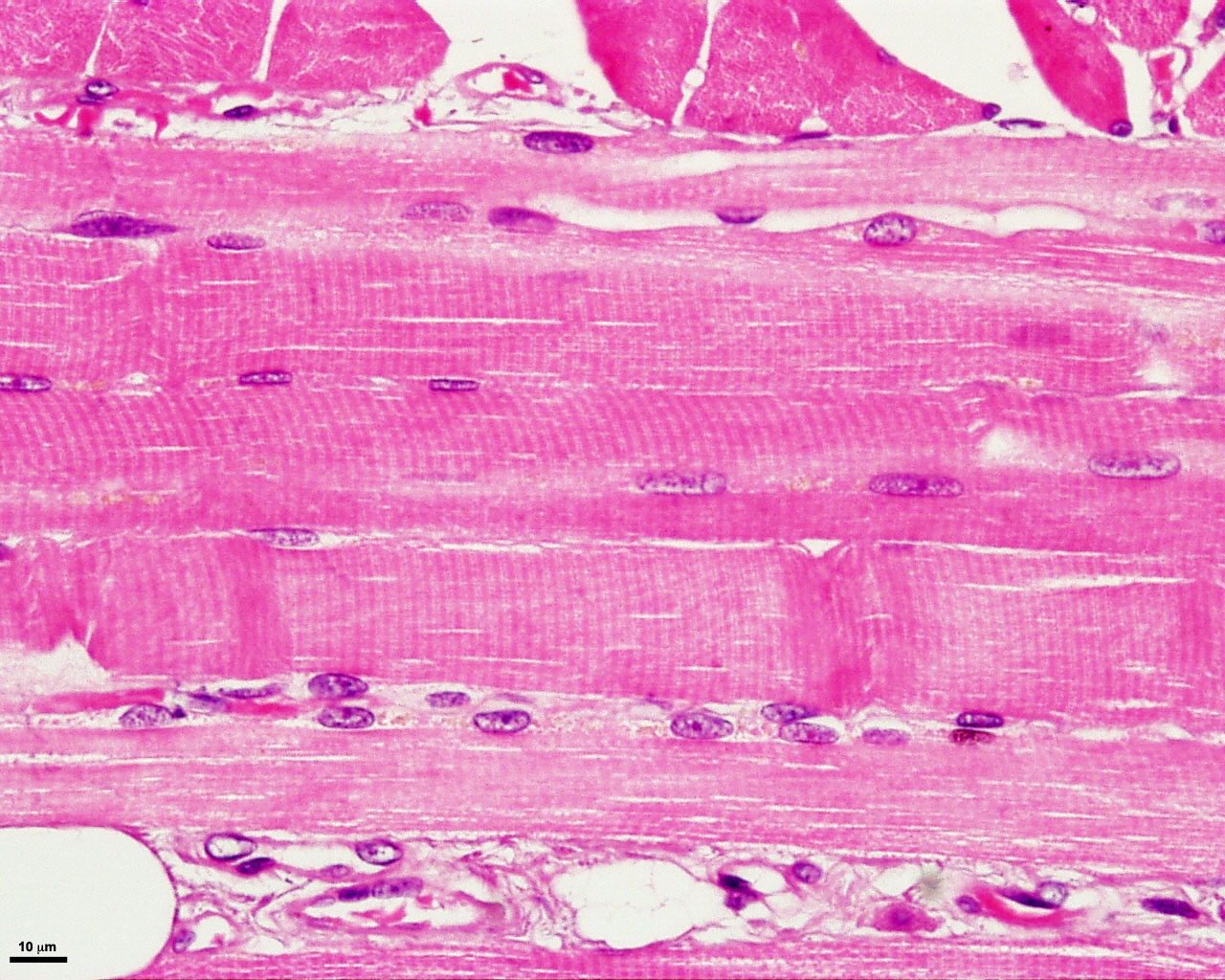
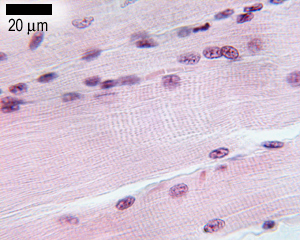
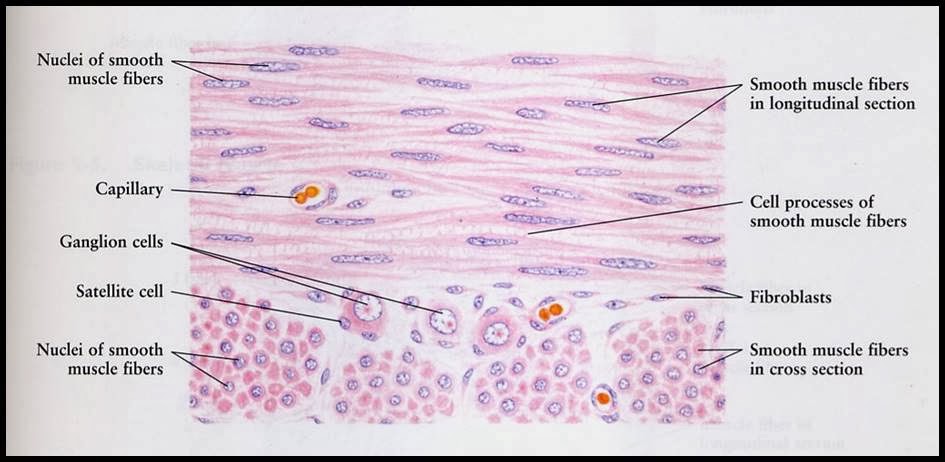
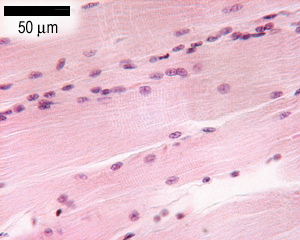
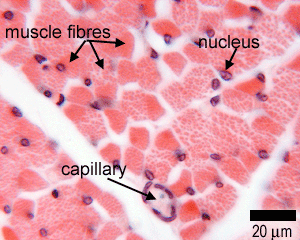
Again note the peripherally placed nuclei in each cell and capillaries within the perimysium. Skeletal muscle can be confused with dense regular connective tissue at low magnification especially 40x. Skeletal muscle cells contain similar components and structures as other cells but different terms are used to describe those components and structure in skeletal muscle cells. Skeletal muscle anatomy 1 levels of organization muscle whole organ fascicle portion of muscle muscle fiber single muscle cell myofibril muscle cell organelle sarcomere portion of myofibril myofilament part of sarcomere 2 muscle organ of muscular system contains.
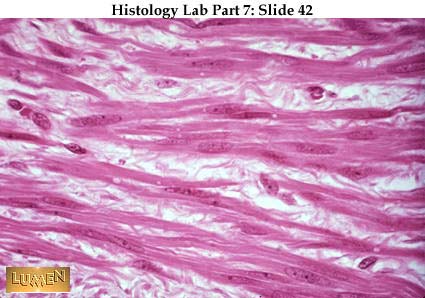
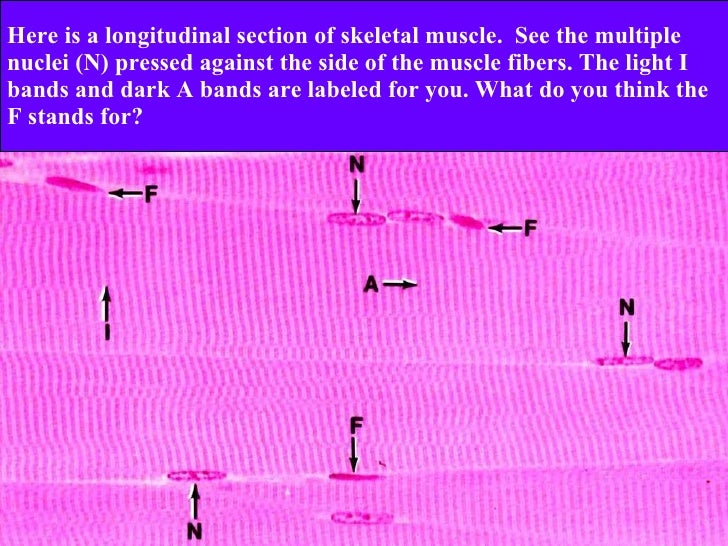
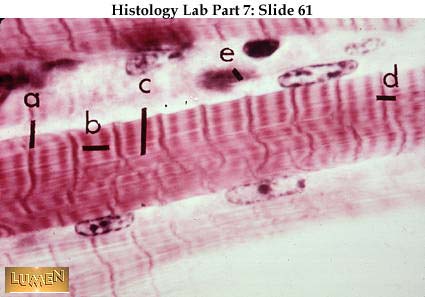
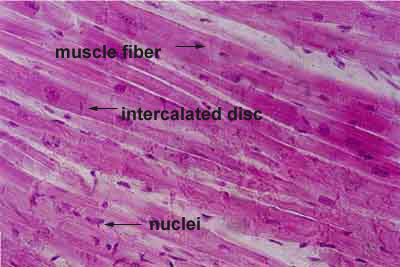
Longitudinal section this is a longitudinal section of skeletal muscle fibers. Skeletal muscles maintain posture stabilize bones and joints control internal movement and generate heat. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. Excitable tissue responds to stimuli through electrical signals.
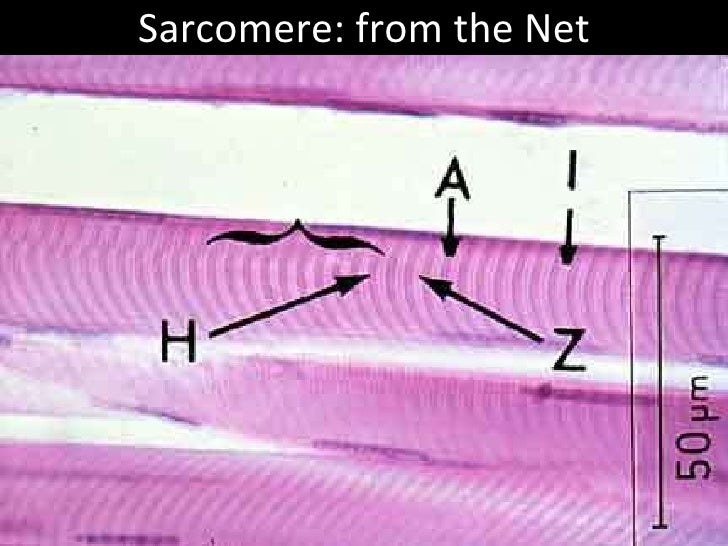
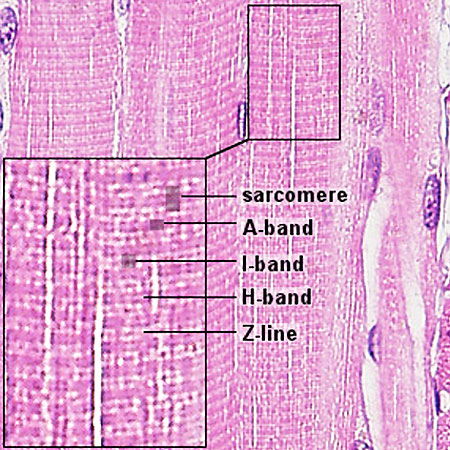
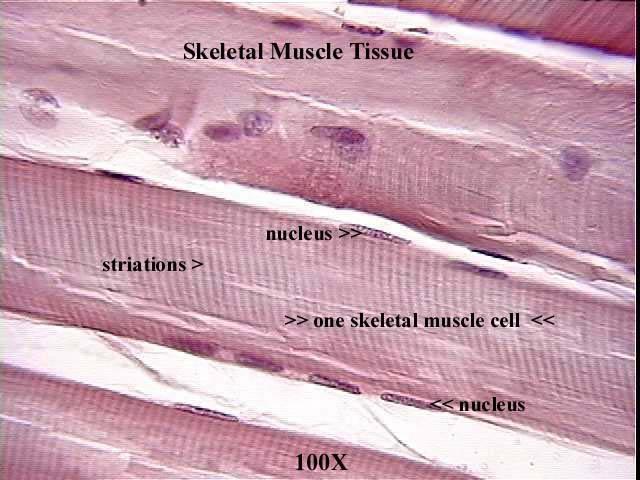
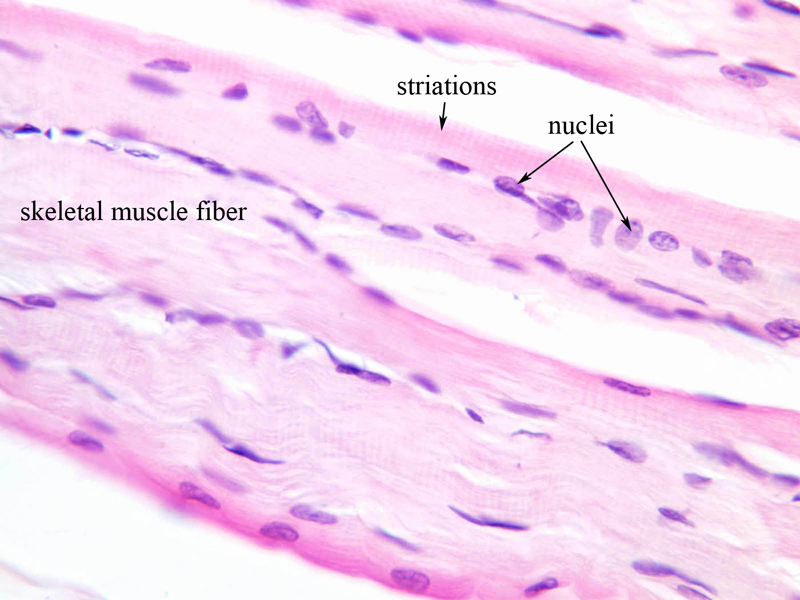
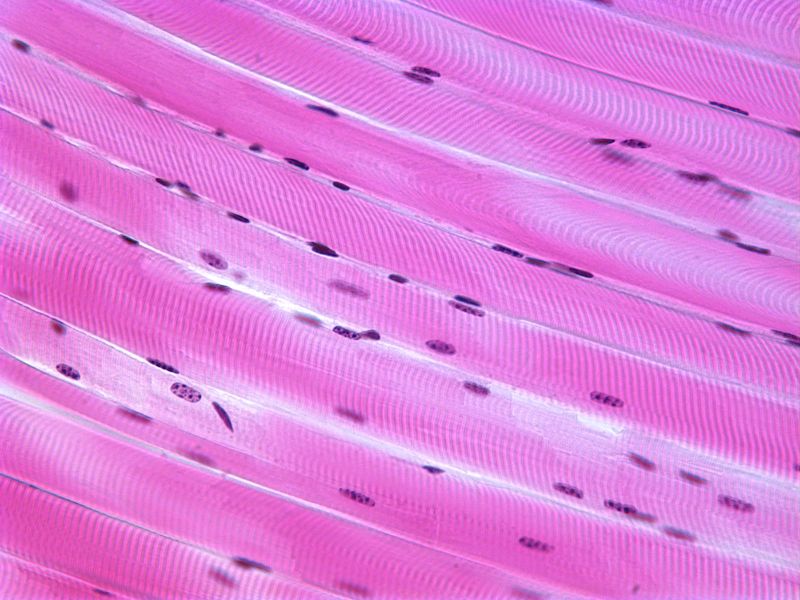
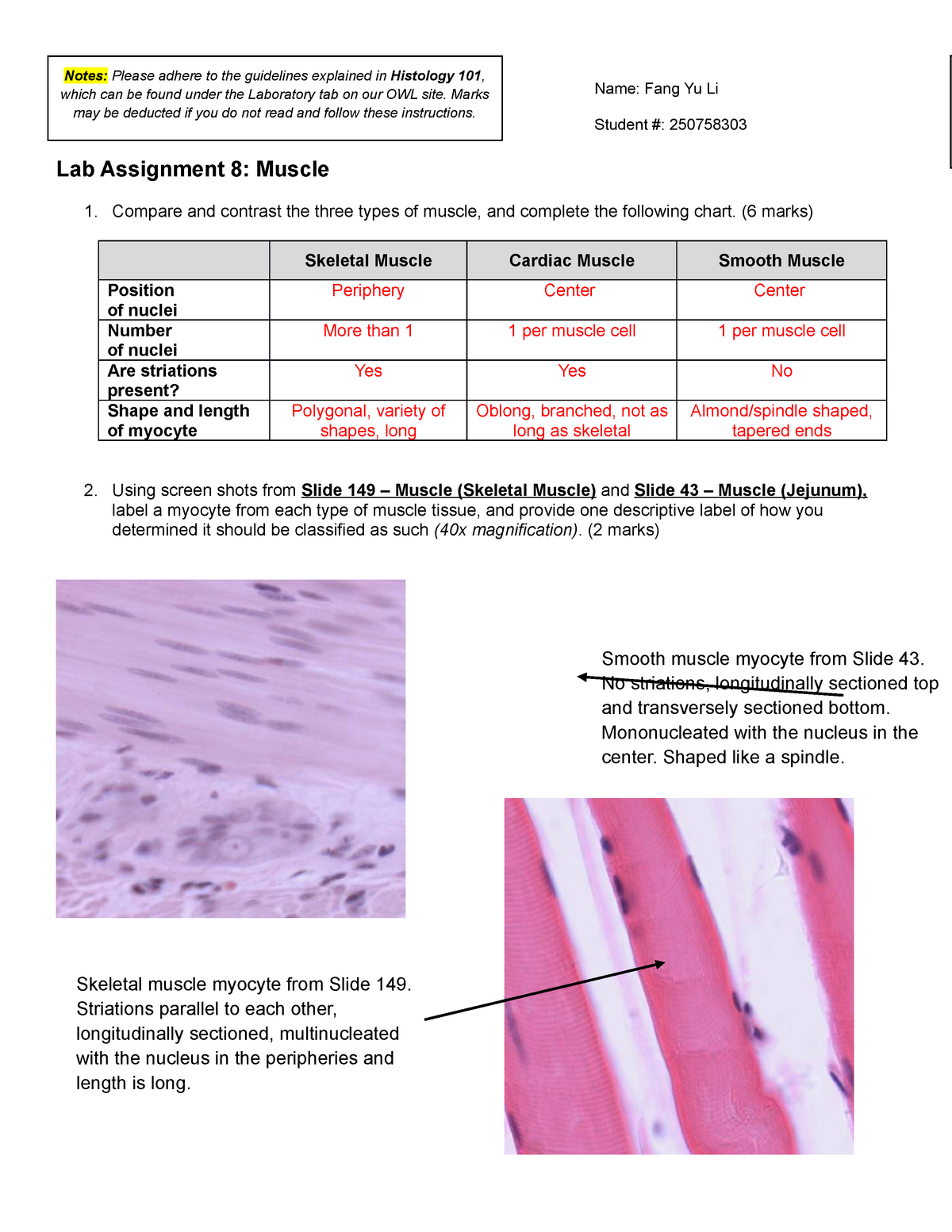
Individual skeletal muscle cells appear as round or polygonal shapes separated from each other by a thin layer of connective tissue the endomysium which appears white in this slide. The skeletal muscle fibers are long and multinucleated. Observe the striated pattern of skeletal muscle. Actin thin filaments being drawn together by myosin thick filaments.
Its cytoplasm is known as sarcoplasm. The endoplasmic reticulum is called the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The plasma membrane of skeletal muscle is called the sarcolemma. Contractile tissue is able to generate tension of force.
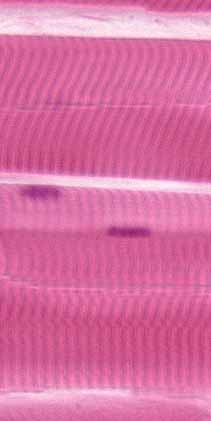
This regular organization gives the muscle. Muscle cells connective tissue blood vessels nerves contractile units covered by. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons and they produce all the movements of body parts in relation to each otherunlike smooth muscle and cardiac muscle skeletal muscle is under voluntary control. There are three major types of muscle and their structure reflects their function.
They stain the same color and the skeletal muscle cell nuclei are flattened just like the fibroblast nuclei in dense regular connective tissue. This regular arrangement imparts a cross striated or striped appearance. In this image you are looking at three bundles of skeletal muscle cells fascicles. Skeletal muscle also called voluntary muscle in vertebrates most common of the three types of muscle in the body.
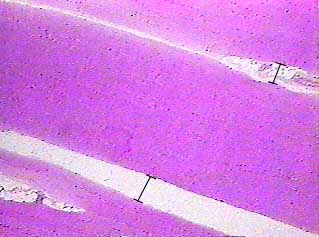
Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles.


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3489/pOHrvgfiIN5rVB0lDf0Tqg_Sarcolemma.png)


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13939/LNOsY5VQ7ADcaM1g9m5g_Cardiac_Muscle.png)









:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/histology-of-skeletal-muscle/CCA8JH8f29ZhIfXBU6FQ_09gjtxSIpcGC6ni5oqNdg_Striations.png)


:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/7173/Skeletal_muscle_01.png)
















:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3490/5heSmCkewUh8Qv1PWQNM2Q_Z_Lines.png)